Abstract
To discuss the Network Application Layer and its uses in the areas of Telecommunications, terminology must be clarified to ensure the concepts can be of use and for whom. A network application layer is a conceptual depiction of part of an unseen architecture to simply show that it is separate, in that, not all people or systems see or have access to all pieces and parts. It can be easily explained as the user end, backside, and middle parts, but some systems are in fact more layered and complex, with interconnected parts spanning across many varied systems, regardless of type. This paper focuses on the Voice Over Internet Protocol System, a new computerized telephone system, compatible with older systems and devices. The complexity and design can only be broadly explained because it is a world-wide system, but well understood when an architect or analyst has either visual or technical on hands understanding of older phone systems, its processing and routing centers, along with new Network Technologies, such as Wide Area Networks (WANs) and the Internet.
What is VOIP? It’s a Phone System that uses the Internet System.
Application
Application software is computing software designed to carry out a specific task other than one relating to the operation of the computer itself, typically to be used by end-users. Examples of an application include a word processor and a media player (Wikipedia, 2021). It also means the action of putting something into operation, “the application of general rules to particular cases (Oxford Dictionary)”, in fact, the word application, has more than 3 meanings, which must always be taken into consideration when using information systems. The depiction of how these systems work, in a layered manner does not truly show “how it works” but gives a visual to understand they are separate and categorized. It is not detailed in the OSI or TCP/IP Model to explain how the Network Application Layer works. Because Data Visualization and Learning is the “single best way our brain processes information (Turban, Volonino, Wood, 2015), some visuals are presented, but nothing closely capable of teaching how a Network Application is designed and how it manages a telecommunications system.
The Model
Both the OSI and TCP/IP diagrams in the figure below show the Application Layer, separate from the Network. The OSI Model separates the Application, Presentation, and Session layers, while the TCP/IP Layers combine those layers. The Application Layer in some workgroups have referred to a “Network Application Layer” which is where and how the Network is managed, to include the Applications that run on the network. Layered systems assume they work on top of another, which is not an accurate depiction; they work interchangeably across each layer, simultaneously together with some requiring a specific type of operating system or device to use properly. Access controls were often running inside those applications. With other access-controlled systems, such as Windows Operating Systems, they are managed differently – on a top layer where access is managed on the TCP/IP level, rather than what is located on the host machine. It is not possible to manage security on incoming an outgoing traffic without in-depth knowledge of security protocols, managed on both the Application layer and the TCP-IP.
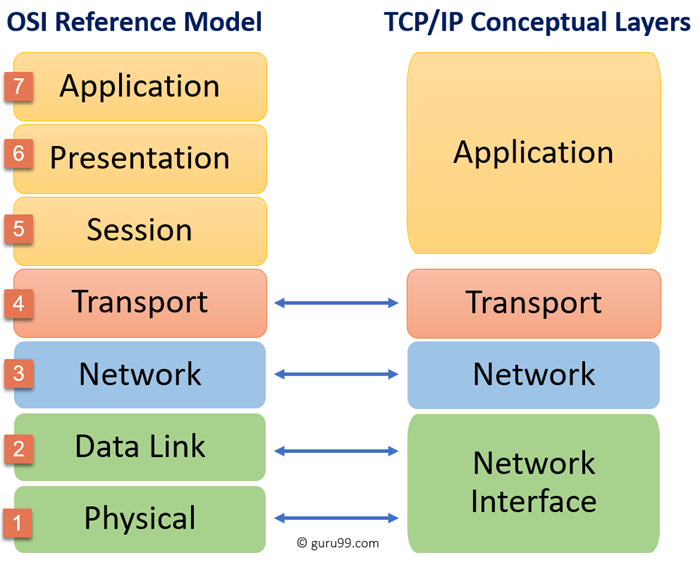
Figure 1 – OSI vs TCP/IP Models – 2020
Telecommunication Network Applications
A network application for Voice Over IP systems is a combination of software and hardware used to manage a phone calling network. Advanced systems include more than just the voice, it includes video, and other data streams, with potential to change and manage air quality and presentation of material. There are some systems with potential to effect perception and mental awareness or expression; most only textually based data systems, created by Microsoft. To explain the types of expressions, one must first review mathematical equations and consider how information is managed and transformed from audio, to numbers, to data bits, and pixels, beyond just one’s email address and phone number. Voice Over IP has great potential for the future, but because of its naming convention, it limits it to just audio systems, when it is capable of so much more, creating another deceptive system or the necessity to rename, perfect, and promote or implement another type of communication system.
Before it can become a more advanced solution, it requires documentation and explanation of how it affects perceptions, moods, health, and behavior beyond just the “wanted vs. unwanted, manual call blocking vs. advanced filtering database include/exclude, declarative programming protocols, and preferred methods of sending and receiving.” Therefore, dissection of the term “application” is necessary because it applies to more than one area: 1) How it is used, and 2) What is used to obtain a position, and 3) Software used to manage an information system. It must be understood that one’s position is vocalized as a decision or perspective with application to more than just a job, but also one’s opinion or decision on a matter. Its resounding or scientific effects beyond a one-to-one communication system must be considered and closely evaluated for similarity and use, especially in global or regional broadcasting systems.
A simple scenario is easily understood by explaining how a system can possibly change the visuals of what is being sent and received when a connection or call is made. Much work has yet to be done on permit and exclude programming, as well as pre-defined or changeable preferences. As the system currently stands, simple still photography is used, with options to see live video. Additional work required is time, location, and information management of not only breaking the sound barrier, but running past calls or events, with management, using both physical human and computer memory. Telecommunications is and was limited to only phone conversations, but some more sophisticated systems can virtually connect for short sessions using time and date specific parameters. Health is of the utmost importance and consideration, due to its potential uses and value.
Wide Area Network (WANs)
The application used to manage the network is not as simple in a Wide Area Network because it includes a larger region and more people. One of the best functions of a WAN is the ability to include or exclude unwanted contact or people, the dissection of information or culmination(s) and summarizations of information. The ability to auto dial and send or receive information across a larger region in consistent formats, which was often the function of a Television Broadcast. The Internet and other systems allow for better use and management of information, in multiple formats, such as TV Broadcasting, Screen casting, Telecasting, and Information Management. Statistics are better captured using computerized advanced database devices, but user controls must change to allow for better programming, viewing, and listening or communication experiences.
Security
Security is advanced and dangerous because one layer could prevent another layer from sending and receiving traffic or omitting or sending too much or the wrong information. This type of security does not currently apply to Voice Over IP Systems (VOIP), such as Skype or Skype for Business, yet still available, complicated, and dangerous if the user does not understand application layer security from more than one perspective: those which the user has direct control on overall application access and those that the application has control over. Using the OSI Model or TCP/IP model to detail or describe telephonic access is complex because some systems include sensor devices, physical layers, with advanced data management systems to filter information, which includes air quality systems and other information that can be sent. Rather than to focus on misuse, problems, and risks, its best to discuss how the Voice Over IP System works on the Network Layer.
Hacking and unauthorized access or “information leaks” are of greater concern with software systems management because of the excessive number of steps and applications required to secure a system and the intelligence or competence factor of paid Network Management sites to protect, store, and filter information, beyond automated solutions. Eavesdropping, Wiretapping, and Hacking has been around for years, as well as stealing, misperception, and misuse of words, thoughts, and ideas, therefore extra precautions must be taken to protect information. In the past, hackers focused primarily on vulnerabilities in in the operating to break into computers…now they hack applications (Panko & Panko, 2015).
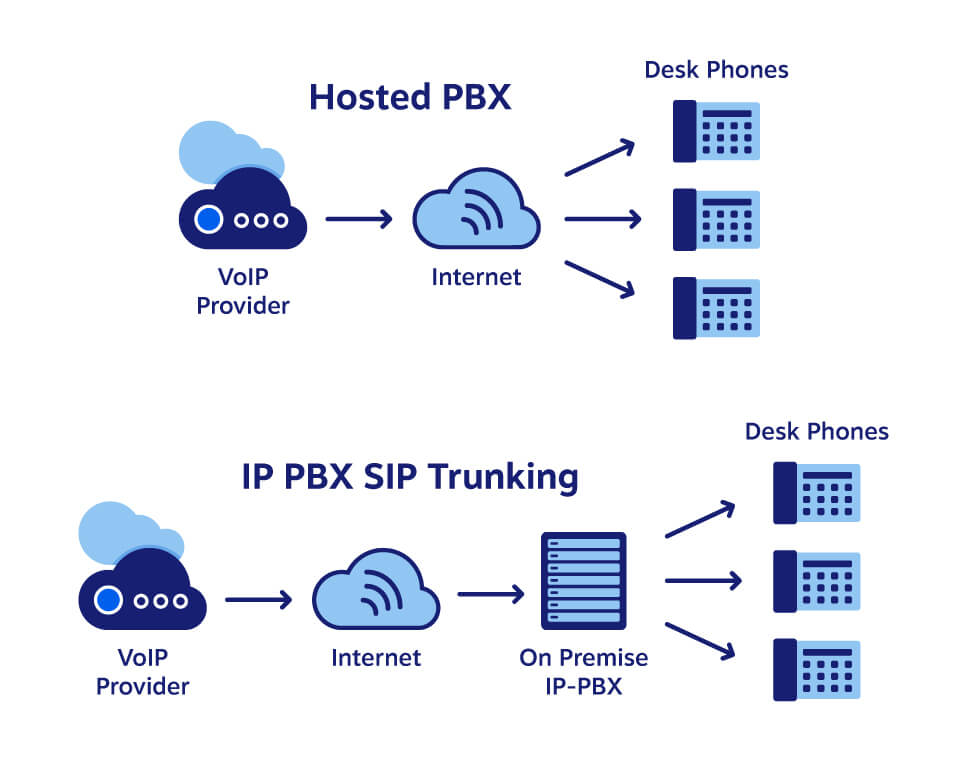
Figure 2 – Voice Over IP System; Courtesy of Surveillance Secure
Although available online as an application, such as skype, it does not run on the “World Wide Web” but must have Internet Connectivity to work. The World Wide Web is not the right location for such as system, in fact, they are more secure and better managed as Networked Software Applications, on servers, and possibly host machines that manage regional call centers, using quality database solutions, integrated with various media formats for personal and business use. Voice Over IP has in fact changed the telecommunication industry, but positioning, use, and acceptance of habitual change and expectations must change. A cordless, battery operated phone with megahertz and range limitations are still used along side wired VOIP systems, but with more advanced systems, there is potential for wireless VOIP with portable devices, using smart phones and small applications for better mobility and management. The critical factors are no longer the type of the devices, but the software and programming designs behind the system.
No longer are bulky and separate telephone lines used to communicate via voice only. VOIP uses the Internet Cabling, Fiber Optic, or existing phone line infrastructure. This integration allows for greater use in communication mechanisms, such as conference calling, live meetings, information management systems, call tracking, reporting, recording, and with the use of advanced geographical systems, improved surveillance, and emergency management. How those networks are managed are done regionally, with various options of personal WANS, LANS, and MANS is still standard, with some more advanced solutions connected to business information applications or software systems for communications and data management.
Explosion of Small Applications on Mobile Devices
The rapid explosion of Small Applications for Mobile Devices was exciting for Smart Phone users and an amazing accomplishment for mobile device operating system companies and application developers. It made a large amount of applications available at low cost, but nothing of great value and real intelligence was added for the business industry that did not require significant amounts of time in programming specifically for a mobile use and integrated with business applications or software. Our industry still operates on stand alone, manual entry systems. Some HTML 5 applications sort of changed that, using Internet Application Programming methods to make accessible on mobile devices. Industry has yet to provide a set of standard business tools and demands too much personal or professional programming for every business, still making IT a costly, yet highly profitable, yet vary dysfunctional and disorganized industry. The concern is the massive amounts of applications, security, viruses, and missed opportunities for integration, automation, improved business functioning and socialization.
References
Oxford Dictionary, “Application,” accessed via the Internet at
https://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/us/ on May 30, 2021
Information Technology Management, 10th Ed., 2015, Turban, Volonino, Wood, pg. 51, 52
Business Networks and Data Security, 2015, Panko & Panko, pg. 378
