Goal of the Proposed Research Project
First, the research project must be correctly referred to as a formal study or dissertation to emphasize the importance of collegiate works which follows a different process necessary to achieve the goal of obtaining the doctoral degree. It is more in-depth than a report, thesis, or assignment. In fact, it is related to the masters thesis and separate work experience not included in the final publication, which might include reused information in addition to what has not yet been written. It is not a short test at the end of a class, school year, or even report written solely for and learned from a formal degree program. The problems identified and solutions created in the study will go on after the degree is conferred, and includes years of past and present work learning experience, in both paid and unpaid positions at various federal, state, and local organizations, agencies, and institutions, wherein, we’ve never been explained the difference, but understand they have different missions, jobs, ethics, goals, standards, and computer systems. In order for it to be better understood, the thesis does not have to be read, but the student must utilize information from all areas impacted or related to those in the thesis and incorporate it into the dissertation, as well as any other relevant published works and useful report studies.
It must be clarified that while the University chose to call it a ‘project’ in a research methods course, the term requires correction and further explanation that there are many types of projects of varying scope, lengths, and impact on many different levels in different areas, as already explained and possibly already known from earlier coursework or experience. The meaning of a project is varied, depending upon age, therefore it must be re-explained that this is not a small project designed where a child might immediately understand its importance and size, where the size refers to how large the problem is, how small the solution is, and how many systems are affected by it. Because the word “Project” was used and is viewed as an incorrect reference and technical term related to the type of study, it requires much more possible wasted time in explanation, causing unnecessary, but possibly still beneficial transformational frustration. While reading previous works is helpful, it is not required, but previous course completion is required to begin or complete a master’s thesis in the subject area.
Children and young adults would not understand it if they have not learned or been exposed to account management from several areas of varied systems verification processes and laws involved: identity, financial, internet software systems and psychological areas related to the subjects included in the research study. Because of this variance in knowledge, exposure, and understanding, the dissertation will be written with a goal to write where all audiences can effectively learn and understand the problems and the solution without using computerized tutorials or scholastically based programs, unless an independent party or educational system chooses to do so using different materials and media than what will be used in this study. The goal is to provide the right access to the right information, while protecting access in the right areas because information management involves security and other matters that must be safeguarded and sometimes kept from the public.
A learning goal for a child or young adult related or used in this study is to understand associated non–referenced publications and be able learn how information is expanded, while learning the collegiate formal finalization work product. The work products, while not paid for by corporations or companies are the thesis and dissertation, or reports. Companies don’t pay their employees to study these topics; they sponsor their employees and pay part of their tuition, fund research, and contribute to financial aid to support learning and problem solving in the field of computer science and information technology.
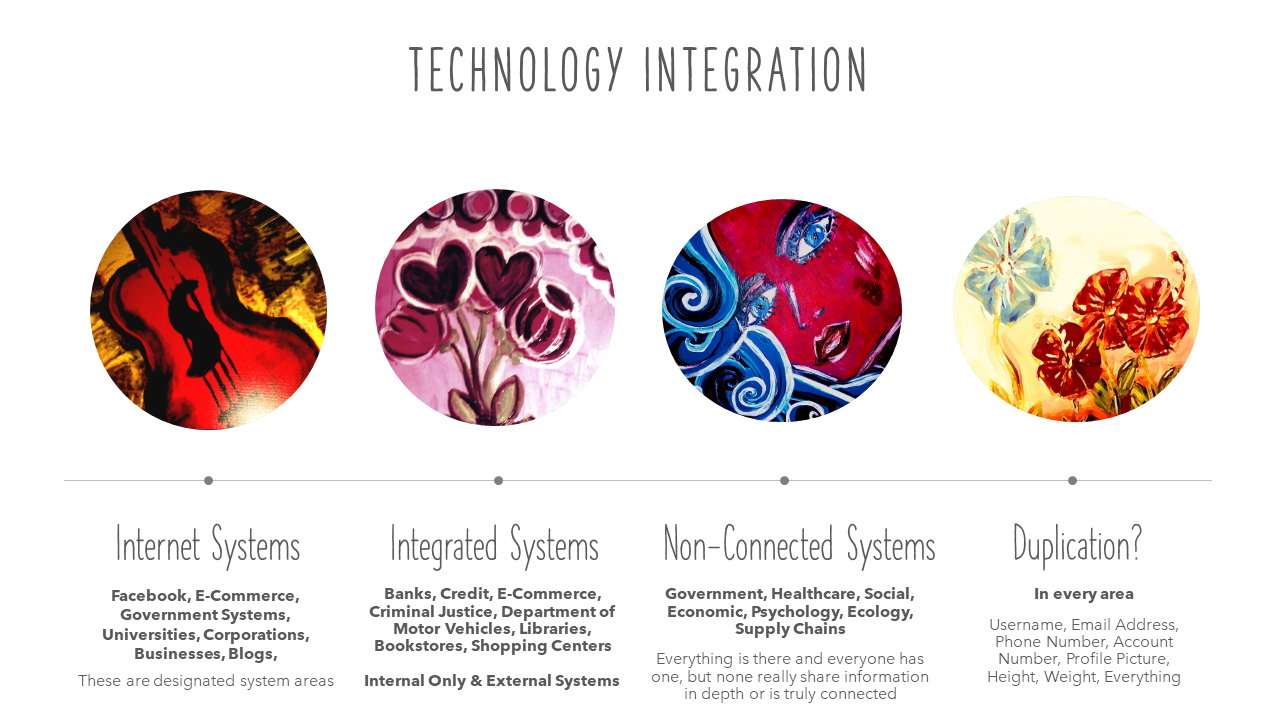
The goal of the research study is to compare in person account management to online computer systems to change the process to reduce risk, duplication, and constant re-authorization by creating a better authentication program in both areas. It is believed the processes and systems affect the entire world, which is why it must be well designed, understood, and explained who will be impacted and what will be done. Possible solutions involve computer programming, process improvement, law, and policy changes. The goal is to write a dissertation where anyone can read and understand it, without providing every technical detail known by a systems engineer, internet developer, or account manager and human, but enough direction and information that different age groups and education levels understand.
Course Benefits Evaluation (3 Least and Most)
The assignment is to select six courses and discuss which three will be the most beneficial and which three will be the least beneficial. The courses have not yet been completed, but a short summary read which includes what will be taught, not what will be learned, assigned, or completed. A student cannot effectively speculate or forecast which courses will be most or least beneficial from future learning based upon a short summary of what the course is about, but they can discuss how it relates to and benefits the research area: Identity and Account Management: In Person and Software Systems, as well as how it relates to previous work and course completions.
Three Most Beneficial and Relevant Courses in the Doctoral Program:
RSH901 – Techniques and Interpretation for Advanced Statistical Research: “With data explosion, data analysis methods using statistics play a fundamental role in the scientific world and industry. Data from multiple sources are common as well. However, we all know that more data does not necessarily imply better information. Extracting valuable information from a mountain of data requires statistical, computational, and analytical skills. Therefore, it is imperative for students to learn how to analyze their data using statistics and derive inferences and model the data that is being used in the thesis.” (Aspen University, 2022). An explanation and correction to the course program is required to differentiate a thesis from a dissertation. A thesis is often completed in Undergraduate or Master’s level courses, with a similar design, while a dissertation (sometimes connected to other studies as more in-depth research), such as “Profile Management, Masters Thesis” is related to the subject area, where the dissertation will solve the problem in greater depth, using formal statistical calculations.
DCS906 – Automata Complexity Theory: The theory of computation or computer theory is the branch of computer science, theory, and mathematics that deals with whether and how efficiently a problem can be solved. The field is divided into two major branches: computability theory and complexity theory. This course will introduce theories, terms, and applications relevant in the area of computation as well as require doctoral level research and writing in order to understand the material in the broader context of computer science.
All courses are beneficial and none will be considered least beneficial.
- DCS901 – Discrete Mathematics for Computer Scientists
- DCS901 – Discrete Mathematics for Computer Scientists
- DCS902 – Concurrent and Distributed Systems
- RSH901 – Techniques and Interpretation for Advanced Statistical Research
- DCS903 – System Metrics & Risk Management
- RSH910 – Research Design and Methodology
- DCS904 – Modern Compiler Design
- DCS905 – Simulation and Modeling
- DCS906 – Automata Complexity Theory
- RSH912 – Introduction to the Dissertation
- DCS907 – Algorithm Design
- DCS908 – Computer Ethics
- DCS909 – Artificial Intelligence
- RSH916 – Problem-Based Research in Action
- DIS995 – Dissertation I: Concept Paper and Doctoral Committee Selection
- DIS996 – Dissertation II: Literature Review
- DIS997 – Dissertation III: Methodology and Ethics
- DIS998 – Dissertation IV: Research and Results
- DIS999 – Dissertation V: Conclusion and Oral Defense