[responsivevoice_button]
A short analysis of technology innovation, implementation, using a multi-disciplined approach for integration of medical and home computing devices.
GAP Analysis – Several Possible Views, Places, and Application
The order of questions or topics of strategic planning are important to the overall understanding of the subject because most plans are not started in the middle or while in progress, where Gap Analysis has started or is underway. Strategic Planning is task that takes place on multiple levels and timelines, and innovation is a similar process of new ideas where both works together in implementation, usually sequentially, but also all throughout the process. Because employees start or join project teams and programs at different project phases, it’s important they understand what phase the project is in. Gap Analysis has several uses in technology and projects, with some projects scheduling the work for a specific timeframe and others have the work going on simultaneously. One task of similar work in computer systems that takes place on its own automatic timeframe is the defragmentation of a storage system, which is a task of ‘reorganization.’ When a company or “organization” is going through a ‘reorganization’ or a ‘gap analysis’ they are in a review phase in need of moving things, people, or projects and money around for improvements or to meet other demands or needs. On another level, one might consider a Gap Analysis a DNA Marker Review of Dental Imprints in need of improvement or change during regression analysis or an accident report review of an employee criminal case. Another level of Gap Analysis, also of importance, is the brand name clothing of off-duty employees or officers and their dependents or family members in connection with a legal case or a matter for review of style preference or choice semi-professional wear. Some companies can and should have information on this level, while others shouldn’t because they include personal matters or matters of tracking dysfunction and misuse, by poor system automation and organizational management. Gaps in employment and dates are another consideration for short analysis during pre-employment screening, interview, and project phases. All these tasks and uses are important types of Gap Analysis, as is another type, which is reviewing gaps or areas where project resources are needed and unavailable, which require the hiring of new professionals and sometimes includes delays of project milestones and timelines. Gaps in understanding or presentation of material is another thing that necessitates Gap Analysis; perhaps because a section of information has been removed or is missing that is critical to the understanding and functioning of the material or the learning process. Gaps in memory are considered a brain dysfunction, or lapse, where information might still be found if items are/were prioritized, removed, or moved to another area. If Gap Analysis is to be successful, it must be strategically planned and scheduled, with a good understanding of its applicability and purpose. A five-year strategic plan is difficult and often high level, with long term goals set that affect entire teams or the whole company, not often managed with day-to-day operational considerations, but faulty planning and project management can cause changes in the higher plan, thus its imperative to clarify what part of ‘strategic planning’ is to be analyzed and prepared and on what level with regular review timeframes which should always include a Gap Analysis. Gap Analysis as a ‘defragmentation’ is even more important, but not commercially used or referred to as an ‘organizational management’ method of storing files and documents. There is in fact, no strategic direction or best practices written for the organization of files or media; they are individual tasks with a ratio of pc:user. A change in this process is accomplished by a larger project, called Cloud Computing or Software Implementation to control how things are done and placed. Even with Cloud Computing made available, options are still plentiful and require a strategy. A Gap Analysis task to complete the computerized defragmentation automated process is not necessary because the automated process is a simple schedule task, and it does not manage missing artifacts, open areas, or positions in need of ‘filling’ or filing and because human organization efforts are different than operating system functions of managing memory and resources. A computerized brain scan image can solve memory gap problems, but not without further development of an imaging system with software, as well as several full tests and gap analysis beyond ‘refilling positions’ or replacing memory with old or new memories, files, or images of lesser or worse values. This is an area where psychological evaluations are required, as well as standards for brain management; often considered a natural self-function, or medical function of managing physical brain tissue using low quality imaging systems.
The organization of topics, such as Gap Analysis within Strategic Management is not considered dysfunctional if a strategy is designed post Gap Analysis and completed because of the results of the Gap Analysis. It is considered dysfunctional if the strategic planning is developed around the computerized task of storage Gap Analysis where the human solely initiates and schedules the task for automatic organization. An example of brain memory resource allocation, or gap analysis is reviewing the mind for organization of thoughts or actions, recalling memories, and using lessons learned in planning new activities or working on innovative tasks of improvement. The computer only minimally assists in these efforts currently, but is capable, with a software brain scan to collect and use best practices and ideas for improvement. Those ideas are currently available, but must be self-initiated, just like the task of defragmentation of the computer’s hard-drive or storage system.
To assume the operating system can strategically manage brain functioning using the ‘defragmentation tool’ is false, as is the assumption that the computer will physically reorganize a full file cabinet of printed documents. The computer can, however, be used to schedule resources and reminders for the task but must be human managed. Strategic planning is designed for larger projects and task, mainly on an individual and organizational level for overall success. Setting up a computerized function on an operating system or several operating systems is in fact a strategic task aligned with an organizational goal, but it is a small task that does not require lengthy planning, documentation, and management, unless the storage systems and operating systems or users are planning a large-scale storage organizational management task, in fact, it is considered a recommended routine task, which affects operations because the computer cannot multi-task while performing this function. If the functionality of the defragmentation or storage organization and memory allocation task grows or changes, then it requires more strategic planning and project management. Gap analysis in that case, can and should only take place when allocating project resources, assuming there are not enough employees or that something has changed that requires reorganization or additional staff and talent. Operating systems complete defragmentation which ensures there are no storage gaps, the memory and file storage systems function correctly, files are stored organizationally, and that the resources are properly used. It conducts corruption analysis for file problems, reviewing size, location, compatibility, and changes in its data that store and manage its authenticity, and size, as well as how it performs, especially before, during, and after movement. The function of defragmentation is completed for optimum performance of the computer resource and its software. The same tasks are completed by human working organizations, to ensure that there is no corruption and if found removed, changed, and improved, and that the working order of storage processing and memory or system functioning is correctly managed for efficient use. The same is true for post implementation; to evaluate changes in size, functionality, and growth, using different measurements, such as profit, professionalism, and education or maturity. If a computerized task or ‘organ analyses’ was found, then it is either a healthcare task, or a fragmented, and unclear or disorganized task of computerized or physical file organization, both of which must be separate and well understood in purpose and function, especially considering the use of ‘bone fragments’ as part of an X-Ray software task. Therefore, task naming and references, as well as use and location is imperative in technology and medical terminology. While a computer’s operating system performs these ‘automatic’ functions, hospital doctors use an image detection system, of which the correction of might be the same strategy, but different type of system. The computer’s operating system performs similar functions, of limited review for only size and type, not quality, color range of/and motion or the movement of files or the account record and access trail of the mover. Computer images of entire operating systems and its contents can easily be installed and copied, reducing setup times for use. The same is true for medical systems, but software and functionality greatly differs. Fragmentation of the different disciplines and combinations requires understanding and specificity; thus, gap analysis of information might be necessary to find missing, empty, or broken parts, or one that potentially corrupts or unnaturally affects another, causing a conflict in terms, which is especially important in storage management and ‘operating systems’ and technology. The same is true for and happens in human resource management, as well as variable storage processes. This information and process area is important because of the necessary bone and imaging systems in Dentistry and other healthcare systems. Moving/hiding X-ray files does not heal an injury, but potentially causes corruption and reorganizing them requires strategic planning, especially in an operational or working system. This part seems fragmented; or out of place, but is applicable because Gap Analysis includes bone references in teeth and other areas. Moving bone fragments requires planning and system updates, on different task and timelines with different systems and connections, such as the brain’s pain center to the bone, as well as the futuristic healthcare pain management system or those that monitor and manage movements throughout the healing process via home computing devices. This area of innovation requires good planning, but in this paper, the invention, or key idea, as it relates to healthcare innovation is not contained in subject headers, therefore readers must read to understand the technology concepts, knowing that this does not include a gap analysis, but innovative ideas and short comparisons of two technological systems and concepts where there is overlap and potential confusion or corruption where one might affect another. Scanning is an option but might result in possible limited and fragmented understanding. In digital imaging, many traits and photographic characteristics can be changed, like facial reconstructive surgery, dental improvements, and other cosmetic or image changes. Such a system that can change it or create medical or surgical plans are preparation systems. If given authorization and programmed correctly, the technology could potentially change actual physical matter from a distance, with more innovative procedures, rather than just scheduling, managing photographic images, document sharing, or running database software. These are innovative ideas, without a strict process or plan for implementation because it requires a proof of concept for further investment in medical technologies.
Implementing an Innovation Strategy
Key inputs from the environment needed to implement the strategy is only necessary for collaborative team efforts where groups of people work on ideas, plans, and make investment decisions. An innovative idea, such as those listed above can be presented, but the audience and deciders, as well as project managers, engineers, and doctors must have a solid foundation in specific areas to be able to compare existing technology, investigate the terminology overlaps, as well as be able to effectively plan and prioritize innovation for more than just ‘image’ purposes, but true and actual changes in mental and physical healthcare systems, beyond paper processing, and records management. Inputs are gathered when others have something valuable to contribute; if nothing of value can be gained from others, in terms of the planning of the innovation, then no ‘collaborative’ effort is needed, and no input must be gathered. The natural human brain and psyche requires approval and for the innovation to be implemented, requires the sharing of the discovery with qualified professionals. Because it’s generalized innovation, the next natural step, then is to choose a section where the imagery, physical body, or brain functionality can best benefit from changes in technology and to strategically manage the innovation research around the specific area. Although it seems like the idea was generated by one, the research task can be completed by one, and presented by one, but the implementation cannot take place with a 1:1 ratio. In order for real change to take place, it must be tested, proven, and then applied to entire communities or test groups. Healthcare, depending upon the area, are individual one to one efforts, and sometimes more than one professional working for the health improvements of one. Streamlining even this effort is an area of innovation of different work, in physical environments, where collaboration, inputs, and strategic planning, innovation implementation is necessary.
Learning and Studying Process
The learning and studying process changes at different levels because of the supportive materials and the assignments, always completed with hopes that affect change with specific outcomes. While the process is generally the same routine, to follow the standard schedule of discussion items and written assignments, the areas of research, understanding, and documentation changes. The ‘learning’ is not based upon other’s research with the intended outcome of application of knowledge in a healthcare setting for financial gain, but for technology advancements. If or when in a work environment, the opportunity to present innovation or apply processes of innovation to technology projects is considered fulfilling, if the right type and level of management is available.
Information Gathering for the Innovation Project
Innovation is designed for firms to outperform the competition, but research and development innovators don’t often have competition when they are the leaders of new products and new inventions. At some point, they will have competition, but during the innovation phase, which is strategically improving company, product, or process performance, information gathering must relate to its strategic goals. Establishing goals and objectives as well as determining feasibility of product engineering or process management or some involvement in the innovative business area is the first step, followed by strategic planning, implementation, and evaluation and control. Critical items for review during each phase vary depending upon the technology and what role the company plays in its development because some innovations are not solely engineered by one single company or corporation. This is where strategic and project management standards are used to manage innovative concepts, prototypes, or development plans, and implementation ideas. The research and required information changes depending upon their roles, responsibilities, and access to resources for each participant. The critical decision for innovation seems to be whether to create, acquire, or merge and a major mistake to avoid in developing plans is to create something new when there is not enough study of existing systems (White & Bruton, 2017). It also seems there is little to no official technical governing and regulatory body for technology innovation, without set rules and guidelines for safety, other than the standards of original manufacturers, and test results of previously engineered products with parts for sale as integration. Although this has been used and standardized in the automotive industry, it is only minimally applied and used in technology. It seems the importance of technology is the integration and management of existing operations, the process of obtaining and implementing the technology, and the performance during each phase to ensure competitive advantage, compatibility, effectiveness, and performance measurements. Many seem to just buy, build, or borrow, without formal strategic planning and risk management. In gap analysis, there are four types of fitness, which are considered key components of evaluation and control: financial, strategic, operational, and relationship. While an improved brain scan MR1 software system with more in-depth brain view, evaluation, control, and understanding of functionality sounds like a good investment for Personal Computing Home Devices, it is less than feasible without improving upon what already exists and studying how the PC can be adapted using its existing design. Understanding the difference in business objectives being research and development for behavioral or massive change in communities, societies, and people, and not corporate competition, building strategic alliances, or acquiring technology for a better performing organization, the right goals can be created, with the right type of organization for the research. This is necessary to ensure the right company is given the right opportunity to improve the technology and not just the original manufacturer or developers of the technology, being the Operating System and its necessary software. This is comparable to brain only analysis without consideration to its connection to the body and its environment.
Project Documents Needed (Fictional Project)
For such a project to even begin, it must have background research, objectives, a problem statement, technology plan, and concept of operations or how the technology is to be changed, implemented, evaluated, and used. The benefits of the technology, as well as the challenges in creating or changing the technology is also necessary. Using management and technology principles for innovation planning is good to remember to balance competitive needs, acquisition processes, and strategic goals and objectives for new venture investments. An outlandish project forecast of how the innovation or change will affect the user population at both home and in the office is also necessary to understand how one system can obtain technology from other systems and work together as a totally integrated high functioning device of a different category at the lowest operating cost, without profitability being the top of its list. For a brain scanning imaging system advancement to be considered a possible area of innovation and integration with home computing devices or mobile photography systems, a technology comparison must be completed, or what is considered a “gap analysis” in both features and functions, design, and what is necessary to implement a system for home devices. Additionally, it requires research and understanding of the differences between psychological and physical matter, understanding the differences between computer viruses, diseases, and other brain dysfunction that is solved by brain surgery or psychiatric medications and other therapeutic options. Objectives of the system is necessary and must not only include a proposal showing the advantages and disadvantages of such a system, but exactly how it works and why it is a profitable investment of more than just monetary value. Responsibilities for programming, changing the systems, and designing new software, or building a new system using combined functionality requires several tests, following standard technology project management and strategic oversight for its success. This includes historical understanding and assessment of past efforts in psychiatry, mental imagery, satellite imagery, and other photosynthesis, and electromagnetic devices. The project must be controlled to be well understood, adopted, and accepted as a necessary system not just for artificial intelligence, but also human evolution in more than just learning. It is unknown whether the study of physical brain matter used in the neuroscience and psychiatry fields are necessary, but it seems that one cannot effectively integrate in the real world as an operational system without the other. Because the terminology and purposes are closely aligned, research is necessary to show how and why the system is beneficial, which includes more than just diagrams to show how parts of the brain are named, but also how the brain functions when connected to a computer system which serves multiple functions of two-way communications of evaluation, trust, knowledge, use, and control.
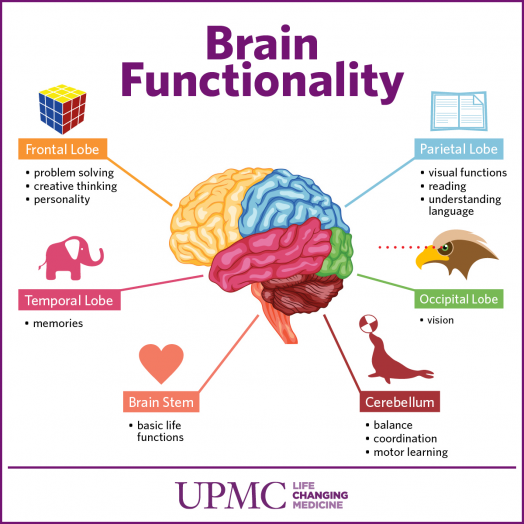
Brain Functionality, UPMC, Life Changing Medicine
Focusing on one area of the brain, being the memory and processing system is an excellent start when seeking to compare it to the computer memory processing and storage system to create the best integrated working system of the two, or to at least understand how they are aligned. Since alignment is a general term, with specific brain to computer monitor position and system, the term alignment must be carefully used and not solely related to ‘strategic alignment’ of people, places, and things for human communication systems, but to include the computing devices and what roles they play and how the plan or system can change each design. This requires understanding and research or design of roles and responsibilities, as well as power and resource allocation structure that might not be what was originally intended, creating a different type of management system than what humanity originally thought or that the creator of the PC and cloud computing devices intended, not by accidental discovery, but because a change in human structure, operations, and management requires innovation. Understanding and managing discomfort during change is a well-known part of technology implementation, where change management is required, because it not only results in job changes, responsibilities, and requires learning, but also because its capable of human evolution and not adaptation or the tried-and-true humanistic routine of war, peace, law, order, business, and social interaction. It’s creation and design also have potential to change the natural need for recognition, and cognitive awareness that humans often crave for new inventions, which has often been how psychiatry and technology have presented themselves in the learning environment and business sector where the names and profitability of the owners or ‘pioneers’ of ideas have often been glamourized, publicized, and rewarded, in history books by the use of their names, bank accounts, and associations with products or ideals. This requires understanding of psychiatric needs for recognition, a natural human need on both sides of the users, the creators, and the documenters of world changing products or systems. Historically, doctors had no effective treatments, asylums were destined to accumulate more and more incurable patients, leaving the staff overwhelmed, demoralized, and with insufficient time or conviction to sustain their ‘moral’ approach. The situation was exacerbated by an increase in the numbers of mentally ill people, especially through neurosyphilis and alcoholism, and by the increasing reluctance of families in industrialized society to tolerate their mentally ill relatives (Cookson, John, 2012). To understand and build an innovative brain integration or development system, one must understand how the psychiatric and psychology discipline, as well as neuroscience separates illnesses, utilizing medication, institutionalization, and outpatient hospital remedies to manage disorders that they have created and think or have received funding for pharmaceutical trials and approval to prescribe medication. The design and structure of the doctor process of medical versus technology doctors is also a valuable necessity to show the differences and how it might change in the future to be a more efficient licensure or qualification proofing process, without heavy evaluation boards and investment processes for something new. The research might disprove the necessity for the boards, evaluations, and prove that the technology process is not yet fully developed and might need to be closer aligned with the medical community, rather than to view it as a hierarchical structure of professional qualification ranking based upon awards, trials, and board-certified inventions or effective trials and tests. Reviewing certification boards for licensure and other qualification metrics can be conducted by evaluating licensing processes and variations in both communities, as well as understanding why some certifications are required to be fully tracked and monitored, with the ability to revoke and punish, especially important during test phases of behavioral management, power and authority testing, as well as perceptual acceptance or ‘grandeurous’ ideals of award and qualification based on beliefs, monetary and educational investment, as well as actual contribution to invention, change, and implementation of certain products or projects. In a specific case in point, there are certifications for medical doctors, lawyers, and technology engineering program professionals, as well as Microsoft specific certified engineers in specialized software engineering all varying levels of education, experience, responsibility, and skill. For new innovations, gap analysis in education or personality fitness, as well as functional ability in applying learned and experiences is necessary, but there are different governing boards, approval processes, and consequential systems for failures, faults, and employee worth in terms of financial status of what is considered earned value.
Summary
Technology innovation and the management thereof, using existing systems, acquiring new systems, or inventing through integration using strategic planning methods requires more than just educational experience gained from reading, as well as evidence beyond timed examinations and board certifications. Although each discipline and its associated process of approval is helpful and necessary, merging any field using technology requires an understanding of the differences, as well as historical review of past efforts by inventors, psychiatrists, world philosophers, and engineers to remain focused not just on personal endeavor and fulfillment or company profit and loyalty, but also the greater goal of discovery and invention.